Emergency shutdown procedures for mold upenders are critical for workplace safety. These protocols, including emergency stops, guarding systems, and proper lighting, minimize risks, prevent accidents, and enhance operational efficiency in mold handling.
In the realm of heavy industrial operations, mold handling stands out as a task demanding both precision and stringent safety measures. The sheer weight and size of molds, coupled with the powerful machinery required to manipulate them, present inherent risks. Among the equipment pivotal to this process is the mold upender, designed to safely tilt or invert molds for various manufacturing stages. However, the potential for equipment malfunction or unforeseen incidents necessitates robust emergency shutdown procedures. These procedures are not merely a formality; they are the cornerstone of a safe working environment, ensuring the well-being of personnel and the integrity of equipment.
The Vital Role of Emergency Shutdowns in Mold Upender Operations
An emergency shutdown of a mold upender is defined as the rapid and controlled cessation of machine operation in response to a hazardous situation or critical malfunction. These situations can range from equipment failure and workpiece instability to personnel endangerment or facility-wide emergencies. The effectiveness of an emergency shutdown system directly correlates with its ability to mitigate potential harm and prevent escalation of incidents. Without clearly defined and rigorously practiced emergency shutdown procedures, even minor anomalies can quickly transform into major accidents, resulting in injuries, equipment damage, and costly downtime.
Proactive planning and implementation of emergency shutdown protocols are therefore paramount. These protocols must encompass several key elements, working in concert to provide a comprehensive safety net.
Key Components of a Mold Upender Emergency Shutdown System
| A comprehensive emergency shutdown system for mold upenders incorporates multiple layers of safety mechanisms and procedural guidelines. These components are designed to work synergistically to ensure rapid and effective response in critical situations. | Component | Description | Benefit |
|---|

| Emergency Stop Buttons (E-Stops) | Strategically placed, easily accessible buttons that instantly halt machine operation. | Provides immediate operator-initiated shutdown in hazardous situations. |
| Pull Cords | Cable-activated switches positioned around the machine perimeter for quick access. | Allows for rapid shutdown from various locations, especially useful in large operational areas. |
| Safety Mats | Pressure-sensitive mats surrounding hazardous zones that trigger shutdown upon contact. | Detects unintended entry into danger zones, automatically halting operation. |
| Safety Interlocks | Mechanisms that prevent machine operation if safety guards are open or not engaged. | Prevents operation under unsafe conditions, ensuring guards are in place for protection. |
| Load Sensors | Devices monitoring weight distribution and load limits, triggering shutdowns if exceeded.| Prevents overloads and instability, protecting against tipping or structural failure. |
| Light Curtains/Safety Scanners | Optoelectronic devices creating safety zones, shutting down the machine upon beam interruption.| Provides non-physical barriers that detect intrusion into hazardous areas. |
| Audible and Visual Alarms| Warning systems indicating an emergency shutdown activation and machine status. | Alerts personnel to the emergency and the machine's state, enhancing situational awareness. |
These technical safety features are most effective when integrated with well-defined operational procedures and comprehensive personnel training.
Step-by-Step Emergency Shutdown Procedures for Mold Upenders
In the event of an emergency, a swift and effective response is crucial. The following step-by-step procedure outlines the essential actions for initiating an emergency shutdown of a mold upender:

- Immediate Hazard Assessment: Upon recognizing a hazardous situation (equipment malfunction, unstable load, personnel endangerment, etc.), operators must first quickly assess the immediate danger and potential consequences.
- Activate Emergency Stop: Immediately press the nearest Emergency Stop button, pull a cord, or trigger a safety mat if applicable. Ensure the activation is decisive and unambiguous to halt all machine movement instantly.
- Verify Machine Stop: Confirm that the mold upender has completely ceased all motion. Observe indicator lights and listen for machine sounds to ensure a full and complete stop. Do not assume the machine has stopped; visually verify.
- Secure the Area: Once the machine is停机 (stopped), immediately restrict access to the mold upender and the surrounding hazard zone. Use safety barriers, tape, or verbal warnings to keep unauthorized personnel away from the potentially dangerous area.
- Personnel Evacuation (if necessary): If the emergency involves a broader threat (fire, facility-wide alarm, etc.), initiate the established evacuation plan for the area, ensuring all personnel safely exit the immediate vicinity and account for everyone.
- Report the Emergency: Immediately report the emergency shutdown to the designated supervisor, safety officer, or emergency response team. Provide clear and concise details about the nature of the emergency, location, and machine status.
- Do Not Restart - Investigate: Under no circumstances should an attempt be made to restart the mold upender until a thorough investigation has been conducted by qualified personnel. The cause of the emergency shutdown must be identified and rectified before resuming operations.
- Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Implement lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the mold upender remains de-energized and cannot be inadvertently restarted during investigation and repair. This crucial step prevents accidental activation during maintenance or inspection.
- Incident Investigation and Corrective Actions: A detailed incident investigation must be undertaken to determine the root cause of the emergency shutdown. This investigation should involve operators, maintenance staff, and safety personnel. Identify and implement corrective actions to prevent recurrence of similar incidents and improve overall safety protocols.
Beyond Immediate Shutdown: Proactive Safety Measures for Mold Upenders
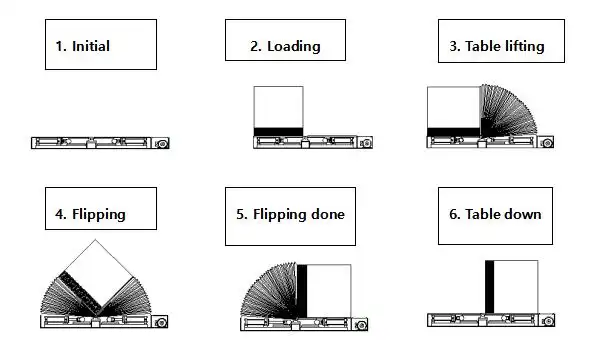
While emergency shutdown procedures are reactive measures for critical events, a truly safe mold upender operation relies heavily on proactive safety measures aimed at preventing emergencies in the first place. These measures include:
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Adhere to a rigorous schedule of preventative maintenance and inspections as per manufacturer guidelines. This includes checking hydraulic systems, electrical components, structural integrity, and all safety devices.
- Comprehensive Operator Training: Ensure all operators receive thorough and documented training on safe operation procedures, emergency shutdown protocols, hazard identification, and proper use of safety equipment and PPE. Regular refresher training is essential.
- Effective Guarding Systems: Implement and maintain robust guarding systems, including physical barriers, interlocks, and safety sensors to prevent access to hazardous areas during operation. Regularly inspect guards for damage and proper function.
- Proper Lighting and Housekeeping: Ensure adequate illumination around the mold upender to enhance visibility and reduce the risk of slips, trips, and misjudgments. Maintain a clean and organized workspace, free from obstructions and tripping hazards.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Mandate and enforce the use of appropriate PPE for all personnel working with or near mold upenders. This includes, but is not limited to, safety footwear, hard hats, eye protection, and gloves.
- Load Monitoring and Management: Strictly adhere to the mold upender's load capacity limits. Implement procedures for accurately weighing molds and ensuring even load distribution to prevent instability.
Restarting Operations After an Emergency Shutdown
Restarting a mold upender after an emergency shutdown requires a systematic and cautious approach. Rushing back into operation without due diligence can lead to further incidents. The restart procedure should include:
- Thorough Inspection and Repair: Qualified maintenance personnel must conduct a comprehensive inspection of the mold upender to identify and rectify the cause of the emergency shutdown and any resulting damage. Repairs should be performed using manufacturer-approved parts and procedures.
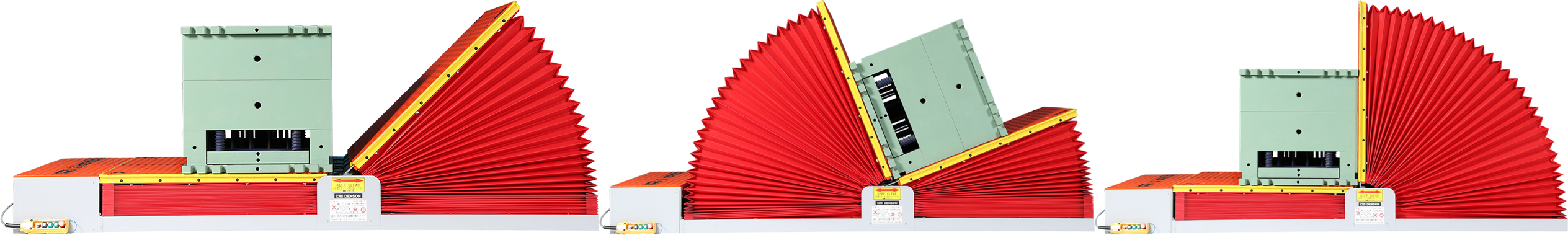
- Safety System Verification: After repairs, meticulously test all safety systems, including emergency stop buttons, interlocks, sensors, and alarms, to ensure they are fully functional and calibrated correctly.
- Pre-Operation Checks: Before restarting production, perform all standard pre-operation checks and inspections as outlined in the operating procedures.
- Supervisory Authorization: Obtain authorization from a designated supervisor or safety officer before restarting operations. This ensures that all necessary checks have been completed and the machine is deemed safe for operation.
- Controlled Restart: Initiate the restart procedure cautiously and gradually. Monitor the machine's performance closely during the initial operational cycles to verify stability and proper function.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Safety Through Emergency Preparedness
Emergency shutdown procedures for mold upenders are not merely a set of instructions; they are a critical component of a comprehensive safety culture. By diligently implementing and practicing emergency shutdown procedures, incorporating robust safety systems, and fostering a proactive safety mindset, manufacturers can significantly mitigate the risks associated with mold handling. This commitment to safety not only protects personnel and equipment but also enhances operational efficiency and overall productivity. Investing in safety is an investment in the long-term success and sustainability of any mold handling operation.






